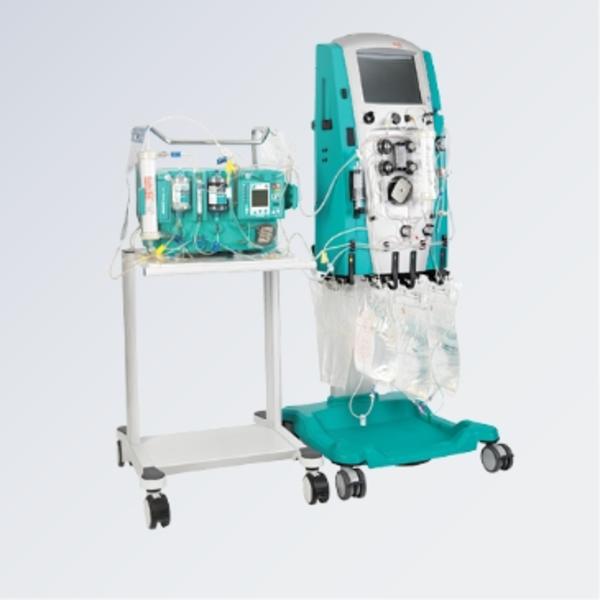
Molecular Adsorbent Recirculation System (MARS) therapy

Tackling the cause of hepatic encephalopathy (HE)
Hepatic encephalopathy is a serious but reversible cerebral dysfunction triggered by severe acute or chronic liver failure. The brain function deteriorates because toxins, normally removed by the liver, accumulate in the blood and reach the brain. A variety of protein-bound substances plays a key role in the pathogenesis of HE.1
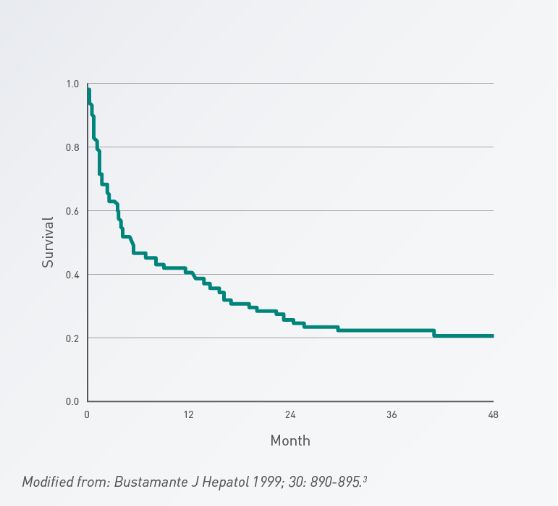
Poor prognosis with HE2,3
The development of hepatic encephalopathy is associated with poor survival in patients with cirrhosis. According to a chart review of 111 cirrhotic patients presenting their first episode of acute hepatic encephalopathy, the survival probability is 42% at one year of follow-up and 23% at three years.2
MARS therapy has shown a clearly favorable effect compared with standard medical therapy for the management of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients not responding to standard medical therapy.1,4

MARS therapy is also cleared for treating drug overdose and poisonings
For drug overdose patients, MARS therapy rapidly decreases toxic levels of protein-bound drugs. This can help prevent ensuing liver damage from the overwhelming toxic effects of the drugs and poisons circulating in the blood, normally removed by the healthy liver.5
Clinical experience and evidence

MARS therapy stabilizes the patient while waiting for the liver to recover or a donor liver to become available.6*
*This intended use is not cleared for the U.S.

MARS therapy reduces portal pressure in patients with acute on chronic liver failure (ACLF)7 which may reduce the risk of variceal bleeding and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) episodes.

MARS has shown to effectively remove bilirubin in patients with either acute liver failure (ALF) or ACLF as reported in several randomized controlled trials.8,9

MARS can improve (decrease) the half-life as much as 280% for drugs such as paracetamol.5

