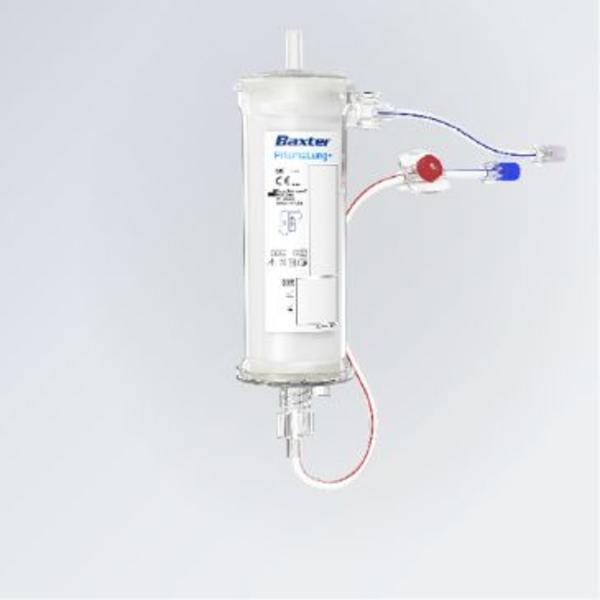
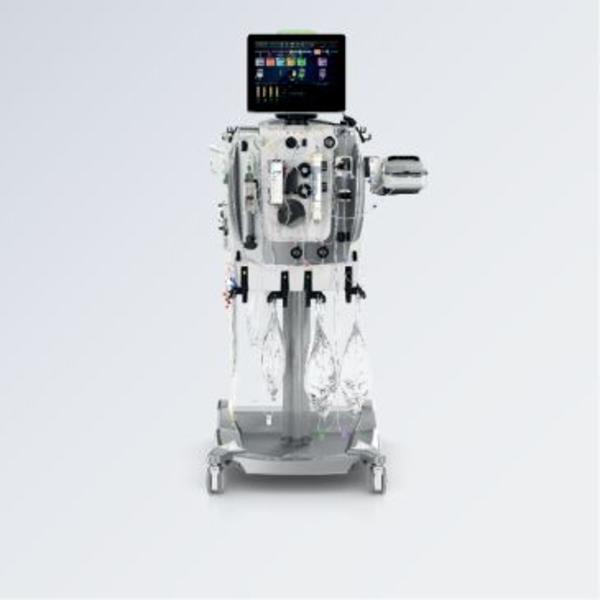
ECCO2R Therapy
Why ECCO2R therapy?
Acute hypercapnia can be a barrier to the use of guideline recommended lung-protective ventilation (LPV) and non-invasive ventilation (NIV) strategies. Extracorporeal carbon dioxide removal (ECCO2R) therapy removes CO2 from a patient’s blood with an extracorporeal circuit to effectively manage acute hypercapnia and respiratory acidosis that can result from lung-protective mechanical ventilation strategies.

Acute Hypercapnia
ECCO2R therapy can effectively manage acute hypercapnia to help bring the clinical and economic benefits of LPV and NIV to more patients.

ARDS
ECCO2R therapy can effectively manage hypercapnia to facilitate the use of LPV or ultra lung-protective ventilation (ULPV) in patients with mild-to-moderate ARDS.1 - 4

aeCOPD
ECCO2R therapy can effectively manage acute hypercapnia to enable the use of NIV strategies which reduce the need for intubation in patients with aeCOPD.

Multiple Organ Failure
ECCO2R therapy can be integrated with other organ support therapies for more efficient management of patients with multiple organ dysfunction.
“….respiratory diseases are a leading cause of death and disability in the world….” “prevention, control, and cure of these diseases and….promotion of respiratory health must be a top priority for health-care systems and decision makers.”
Forum of International Respiratory Societies. The Global Impact of Respiratory Disease – Second Edition. Sheffield, European Respiratory Society, 2017. (Ref 5)
Addressing barriers in caring for your patients
Acute hypercapnia can be a barrier to the use of guideline recommended LPV and NIV strategies:
- Invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) with higher plateau pressures, tidal volumes or driving pressures can lead to ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) and may contribute to multiorgan dysfunction.6 - 10
- Consequently, clinical guidelines recommend using mechanical ventilation strategies to decrease the risk of lung injury in patients with acute respiratory failure, including lung-protective ventilation (LPV),11 - 13 ultra lung-protective ventilation (ULPV),14 or non-invasive ventilation (NIV).15

Facilitating use of ventilation strategies for patients with ARDS
- ECCO2R therapy can effectively manage hypercapnia to facilitate the use of LPV or ultra lung-protective ventilation (ULPV) in patients with ARDS.1 - 4
- ECCO2R therapy may help manage hypercapnia in patients with ARDS secondary to COVID-19.16
- ECCO2R therapy–enabled LPV and ULPV strategies may provide a cost-effective survival benefit in patients with moderate ARDS.17

Enabling use of NIV strategies for patients with aeCOPD
- ECCO2R therapy, at blood flow ≤ 450 mL/min, may help reduce the need for invasive mechanical ventilation in patients with aeCOPD.23
- ECCO2R therapy can help to prevent intubation and IMV in patients with aeCOPD at risk of NIV failure.16, 19 - 21
- Data from a matched cohort study using historic controls indicate that patients with aeCOPD receiving NIV and ECCO2R therapy had a 73% decreased risk of intubation (HR 0.27; 95% CI 0.07–0.98; P = 0.047) compared with patients receiving NIV alone.19

Integrating with other organ support therapies
- Patients with acute respiratory failure often experience other forms of organ dysfunction, including renal failure.20, 23 - 25
- ECCO2R therapy can be used at blood flow rates of ≤450 mL/min,23 enabling integration with other organ support therapies, such as CRRT or blood purification using the same platform.23,24
- Clinicians can provide multiple organ support therapies using a single vascular access, helping to minimize the invasiveness of treatment20,23,24 and reduce the risk of infection for patients with multiple organ dysfunction.26 - 28
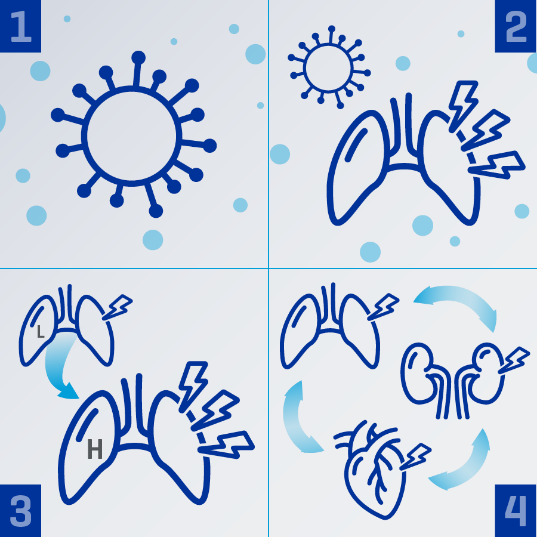
Understanding COVID-19 and ECCO2R therapy
ECCO2R therapy can support the use of LPV by managing elevated CO2 levels:
1. Respiratory cells can become infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus.29
2. Viral infection and a dysregulated inflammatory immune response can both contribute to lung injury.30,31
3. Lung injury can present as type L pneumonia, which can progress to severe “ARDS-like” type H, characterized by edema, tissue damage, and severe hypoxemia.32,33
4. The complications of severe lung injury and its treatment can lead to multiorgan dysfunction, including acute kidney injury.31,34